What's The Difference?
In some ways, thermoforming and fiberglass are similar processes. Both have lower startup costs than other processes, enabling cost-effective creation of lower quantities of parts. But they also have some distinct advantages and disadvantages. Our chart will help you understand some of those differences.

Thermoforming vs. Fiberglass Guide
| Process | Thermoforming | Fiberglass |
|---|---|---|
| Process Overview | A plastic production process that heats a rigid 2-dimensional sheet and uses vacuum and/or pressure to form that sheet against a mold into a 3-dimensional shape. | Fiberglass reinforced resin is formed into 3-dimensional shapes. The resin is applied in multiple layers to build up strength and achieve the desired thickness. |
| Volume | Most cost effective in production volumes from hundreds to mid thousands. | Used mainly in prototyping and smaller production runs |
| Material |
|
|
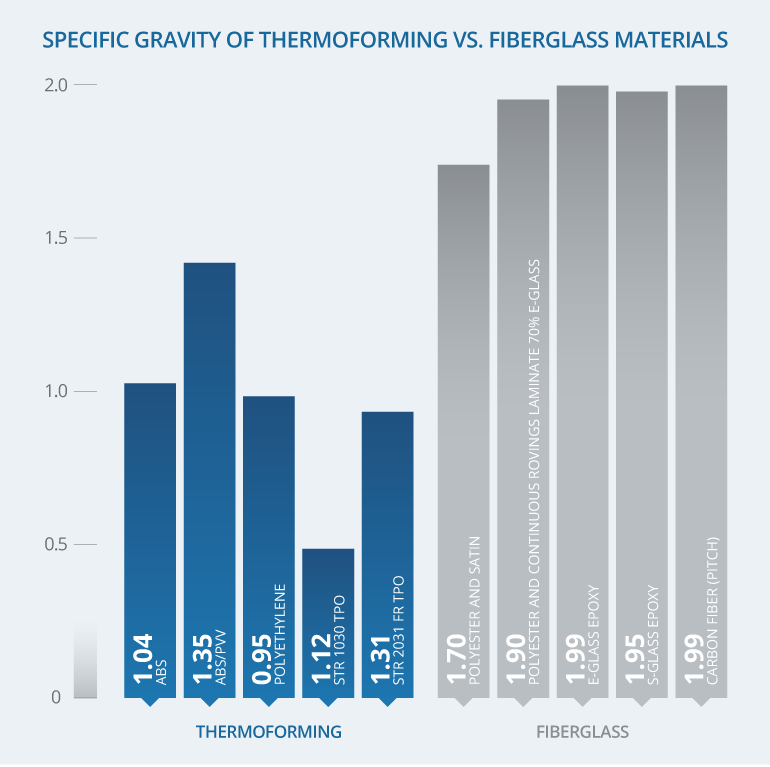
| Finished Part Weight (See Specific Gravity Graph) | Up to 35% Lighter | Up to 35% Heavier |
| Finishing Options |
|
|
| Recyclability | Both final thermoformed parts and excess material are fully recyclable. | The final parts are non-recyclable, and the process uses a significant amount of hazardous materials. |
| Labor Costs & Lead Times | Thermoforming is a highly automated process, particularly at state-of-the-art facilities like Ray Products. Most parts are made from an aluminum tool, which decreases lead times and provides lower labor costs. From a processing standpoint, thermoforming is faster and less expensive in volumes of high hundreds to mid thousands. | Fiberglass molding is a very labor intensive process and often requires multiple tools for the production of a single part which results in slow production output, higher costs and longer lead times compared to thermoforming. |
| Tolerances & Complex Geometry | Thermoforming can support the tight tolerances and complex geometries necessary to create mating parts. | It’s difficult to support the complex geometries and tight tolerances necessary to create mating parts with fiberglass molding. |
| Part-to-Part Repeatability | ***** | ** |
| Impact Resistance | ***** | ** |
| UV Resistance | ***** | *** |
| Molded-In Features | ***** | ** |
| Durability | ***** | *** |
The specific gravity of a material is useful in comparing the weight of different materials. A lower specific gravity will result in a lower weight for an equal amount of material.
By looking at the specific gravity of common thermoplastics used in thermoforming and comparing them to the specific gravities of common fiberglass materials, we can easily see the benefits offered by thermoforming.